The heart is arguably one of the most vital organs in the human body. The heart is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. As the heart pumps blood, it nourishes the body with rich oxygenated blood and carries carbon dioxide to the lungs and out of the body.
The heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels called the circular system, also known as the cardiovascular or vascular system. This organ system circulates the blood vessels, which contain nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from our cells in our body. This provides nutrients, helps your body to fight off diseases, and helps to maintain your body. The vessels are elastic tubes that carry blood to every part of the body. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins return it.
As we get older, the blood flow to our extremities, especially to the lower extremities, is not as efficient for various reasons, like plaque build-ups that will induce and cause various diseases. Peripheral vascular disease includes any condition that affects the circulatory system. Vascular disease ranges from diseases of your arteries, veins, and lymph vessels to blood disorders that affect circulation. In addition, Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a condition where blood vessels outside the heart and brain can spasm, narrow, or become blocked. The following are conditions that fall under the category of vascular disease.
What is Vascular Disease?
Vascular disease, also known as peripheral vascular disease (PVD), is a condition that affects blood circulation. This disorder causes various blood vessels outside the brain and heart to block, narrow, or spasm. Peripheral vascular disease can affect either veins or arteries.
Typically, vascular disease can often cause fatigue and pain. The pain is usually accumulated in the legs, especially when exercising or actively on your legs when walking or working. However, the pain can subside after resting.
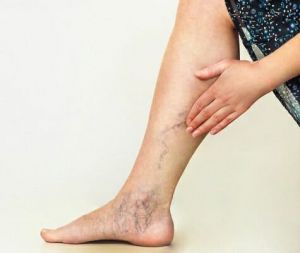
However, peripheral vascular disease is not limited to the legs. The condition may also affect blood vessels tasked with supplying oxygen to various parts of the body. These include blood vessels to the intestines, stomach, kidneys, and arms.
Patients suffering from peripheral vascular disease experience narrowing blood vessels, consequently decreasing blood flow to certain parts of the body, particularly in the lower extremities. This can be caused by the hardening of arteries, also known as arteriosclerosis. In some cases, PVD can also be caused by blood vessel spasms.
In the case of arteriosclerosis, plaques accumulate in the blood vessel and reduce the flow of oxygenated blood to the limbs and other organs. When not managed in good time, the plaque buildup continues and may lead to blood clots, which could block the arteries completely. Consequently, this blockage may lead to organ damage and the loss of toes, fingers, and limbs. This highlights the importance of getting treatment for the vascular disease as soon as possible. The longer you wait, the more adverse the effects may be.
Vascular disease is sometimes referred to as a peripheral arterial disease, and the two terms are often used interchangeably. However, the key difference between peripheral vascular disease and peripheral arterial disease is that the latter only affects arteries –that carry oxygen-rich blood to various organs from the heart.
Statistics from the Center for Disease Control (CDC) reveal that about 20% of people develop the peripheral arterial disease. PAD is the most common condition of PVD. However, other terms used to define the condition include:
- Claudication
- Arterial insufficiency of the legs
- Intermittent claudication
- Arteriosclerosis obliterans
- Non-healing Ulcers
What to Expect from Your Visit to Pedes
ULTRASOUND
ULTRASOUND
Your treatment will begin with an ultrasound examination of your veins, arteries, or both, in your legs to diagnose the presence and extent of the disease. Your test results will be immediately available to review with the doctor.
CONSULT
CONSULT
Once we review the results of your diagnostic tests, our physicians will help you develop a plan to provide you with the best treatment for your disease.
TREATMENT
TREATMENT
Depending on the extent of disease in your arteries or veins, our specialists may recommend minimally invasive intervention and/or prescribe medications to help your symptoms.
FOLLOW UP
FOLLOW UP
It is important to make sure that you return for every scheduled follow-up appointment to ensure that your disease is appropriately monitored. If you ever have any questions or concerns, please call or schedule a follow-up appointment with our staff.




