

When blood moves too slowly in your veins, it can cause a clump of blood cells (a blood clot or Thrombus). Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot forms in the deep vein located in the leg, thigh, or pelvis. While Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is common in the lower leg, it can also develop in other body parts, including the arms. So, how do blood clots form in the veins, and is it dangerous?
To answer this, let us look at how the blood circulates in the body. The blood circulatory system consists of two blood vessels, namely the arteries and veins. The arteries carry blood rich in nutrients and oxygen from the heart, while the veins carry the deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Arteries have thin muscles within their walls that make them capable of withstanding the pumping pressure from the heart. However, the veins have no muscle lining and entirely depend on the muscle movement to take the blood back to the heart.
The venous system in the legs consists of two main veins, the superficial veins, and deep veins. As the name suggests, deep veins are located deep within the muscles. On the other hand, superficial veins are located just below the skin and are easily visible. Typically, the blood flows from the superficial veins into the deep venous system through perforator veins. Both the perforator and superficial veins have valves that allow blood to flow in one direction.
However, when blood travels slowly in the veins or pools in the veins, the platelets tend to stick together. While a blood clot (thrombus) in the deep venous system of your leg is not dangerous by itself, it can become life-threatening when it breaks and travels to enter the pulmonary vein. When the blood clot blocks a pulmonary artery, it decreases the amount of oxygen absorbed in the blood, causing a life-threatening condition known as pulmonary embolism.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is considered a medical emergency. According to the CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention), 10 – 30 percent of individuals who develop leg DVT experience life-threatening complications within a month of diagnosis.
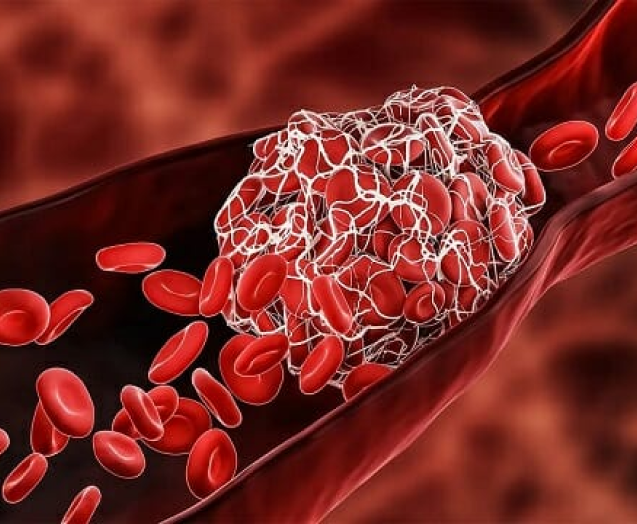
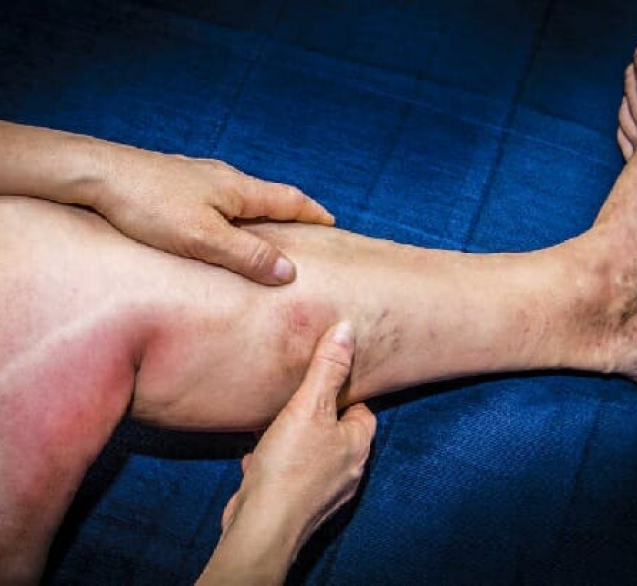
Like other disorders that affect the venous system, some individuals with DVT may not notice any symptoms. However, if the symptoms develop, people with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) may experience the following:
Most often, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) affects only one leg, although, on rare occasions, the condition may develop in both legs. If the blood clot (thrombus) breaks and travels up to the lung, a person suffering from pulmonary embolism may have the following symptoms;
Sometimes, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) develops without a clear cause. However, according to findings done by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), DVT occurs due to one or a combination of the following underlying conditions and risk factors.
Deep vein thrombosis leads to various health cases, including life-threatening conditions such as pulmonary embolism.
If you suspect that you have any of the discussed symptoms, seeking immediate medical intervention is crucial. Your physician will ask you various questions about your medical history and symptoms before performing a physical examination. Some of the tests that help the doctor in diagnosing the condition include:
An ultrasound test is effective in detecting blood flow alteration and blood clots. The doctor uses a handheld device that sends sound waves into the blood vessels and displays the picture on a computer showing the condition of your blood veins.
To get a clearer picture, the doctor may request a venogram. The procedure involves the injection of a special dye that makes the veins appear on X-ray images.
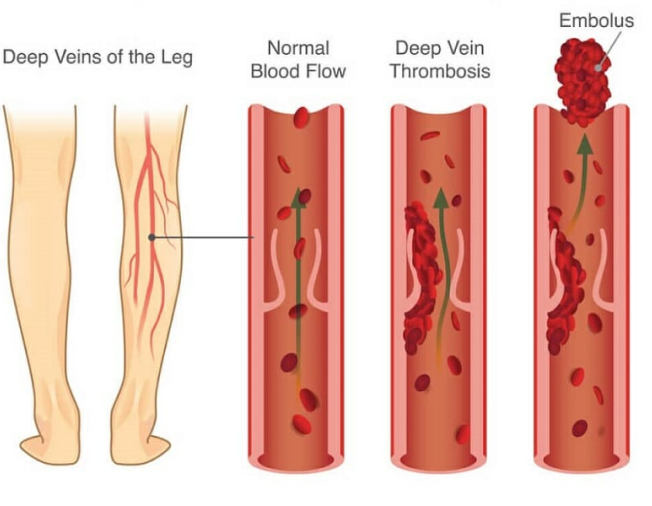
As mentioned, DVT can lead to life-threatening conditions. The main DVT complications include:
PE is a severe DVT complication that develops if a blood clot travels through the blood vessels and reaches the lungs. When the blood clot is stuck, it disrupts the flow of blood into the lungs. A medium-sized clot can lead to intense chest pain and breathing problems. In more severe cases, the lungs can collapse and even lead to heart failure.
People with recurrent DVT are at high risk of post-thrombotic syndrome. An individual with this condition might experience the following symptoms.
DVT is a serious and life-threatenting condition. At our office we will treat you quickly and with urgency. Our vascular will manage your DVT with Anticuagulation Medication or perform a minimally invasive treatment such as Thrombectomy and Thrombolysis.
The physicians at Pedes Orange County devote their lives to saving limbs and minimizing pain. Our conveniently located, state-of-the-art facility is designed for your comfort and utilizes cutting-edge technology to provide minimally invasive treatments. Our vascular surgeons and vascular specialists are board-certified and some of the best in Southern California. Personable staff members make every visit a positive experience, with short wait times and an efficient, streamlined process that ensures you leave feeling educated and confident that you are in good hands.

Vascular Specialist

Vascular Specialist

Vascular Specialist

Vascular Surgeon
Living with deep vein thrombosis symptoms can disrupt the quality of your life. While some may not experience the symptoms, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can lead to life-threatening conditions. At Pedes Orange County, we have a dedicated team of experts specializing in treating DVT. We prioritize your experience to ensure that you get a customized treatment that meets your needs. Our friendly physicians will discuss the steps to relieve the symptoms and stop the condition from progressing from your first visit.
Each treatment plan is individualized depending on the disease stage and other underlying conditions. Additionally, you do not have to worry much about the payment. Most medical plans cover deep vein thrombosis. Before treatment, our staff will talk to your insurance cover or secure the medical coverage whenever possible. So, what are you waiting for? Contact us today, and we will walk with you every step of the way to ensuring that your health is restored.

Your treatment will begin with an ultrasound examination of your veins, arteries, or both, in your legs to diagnose the presence and extent of the disease. Your test results will be immediately available to review with the doctor.
Once we review the results of your diagnostic tests, our physicians will help you develop a plan to provide you with the best treatment for your disease.

Your treatment will begin with an ultrasound examination of your veins, arteries, or both, in your legs to diagnose the presence and extent of the disease. Your test results will be immediately available to review with the doctor.

Your treatment will begin with an ultrasound examination of your veins, arteries, or both, in your legs to diagnose the presence and extent of the disease. Your test results will be immediately available to review with the doctor.

Learn more about our treatment options

Learn more about our what to expect
Return to the interactive body page
Treatments
Diagnostic Testing
Arterial Treatments
Venous Treatments
Women’s Health