Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
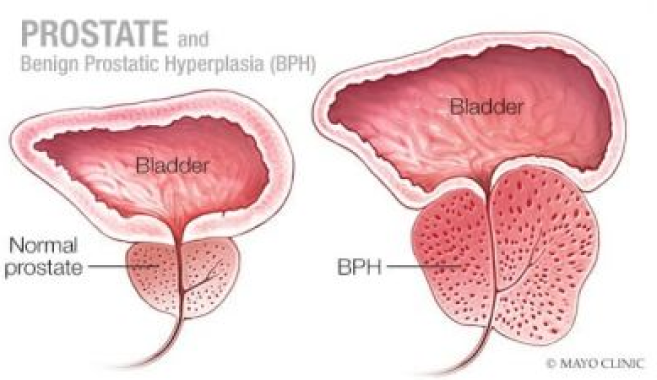
As men age, the prostate undergoes two growth cycles. The first occurs during early puberty, doubling the prostate’s size, and the second begins around age 25 and continues throughout life. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) typically develops during this second phase, where the prostate enlarges, pressing against the urethra and thickening the bladder wall. This leads to the narrowing of the urethra, urinary retention, and incomplete bladder emptying, causing symptoms such as urinary tract, bladder, and kidney problems.
The prostate, a small muscular gland surrounding the urethra, produces most of the fluid in semen and helps propel it during ejaculation. BPH occurs when prostate gland cells multiply, causing the gland to swell and obstruct urine flow. Although BPH is benign and does not cause cancer, it leads to uncomfortable symptoms and complications that can affect quality of life.
Symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
For most people, the benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms are very mild at first. However, the symptoms worsen over time if left untreated. Similar to other conditions, the severity of the symptoms varies from one person to the other. The common signs and symptoms of BPH include:
- An abrupt urinating urge
- Leakage or incontinence of urine
- Dribbling, especially when you are done urinating
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts
- Half-finished bladder emptying
- Nocturia, a condition that leads to increased frequency of urination at night
- Incontinence or leakage of urine
- A delayed or slow urinary stream
- Straining when urinating
- Painful urination
Although less common, a person suffering from BPH can also have the following symptoms:
- Inability to urinate
- Urinary tract infection
- Blood trace in the urine
Most often, your prostate size does not primarily determine the severity of the symptoms. Men with a slightly enlarged prostate can experience severe symptoms than men with significantly enlarged prostates. Sometimes, the symptoms stabilize with time. However, if you experience one or more of
these symptoms, you need to talk to your doctor. BPH is treatable, and often-early treatment helps to prevent complications.
Causes of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
For most men, prostate growth continues throughout life. As such, BPH is considered a normal part of male aging. While it is not entirely clear what causes prostate enlargement, variations in male hormones that develop as we age might be a contributing factor. A family with prostate issues history or testicle abnormalities may put you at increased susceptibility to BPH, in addition to the following.
01
Aging
Benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) symptoms are rare in men under the age of 40 years. By the age of 60, about half of men may experience moderate to severe symptoms. On the other hand, 90% of men aged above 80 experience BPH symptoms.
02
Lifestyle
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH). Regular exercise and the proper diet can help lower the risk.
03
Diabetes and Heart Disease
Heart disease, diabetes, and beta-blockers are shown to increase the risk of developing the condition.
Complications of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia (BPH)
Most men suffering from BPH do not develop complications. However, acute urinary retention can lead to severe complications. Common enlarged prostate complications include:
- Sudden inability to urinate.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs).
- Bladder stones.
- Bladder damage.
- Kidney damage.
Diagnosing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Your Pedes Orange County doctor will begin the diagnostic process by asking detailed questions about your symptoms and performing a physical examination. The first examination usually includes:
Digital rectal exams are a critical diagnostic tool for BPH, allowing our physicians to assess the size and condition of the prostate gland by physically examining it through the rectum.
Urine and blood tests are essential in diagnosing BPH, providing valuable insights into potential urinary tract infections, kidney function, and prostate-specific antigen levels.
Urinary flow, dynamic, and pressure tests are pivotal in diagnosing BPH, as they measure the force and pattern of urine flow, identify blockages, and assess bladder pressure.
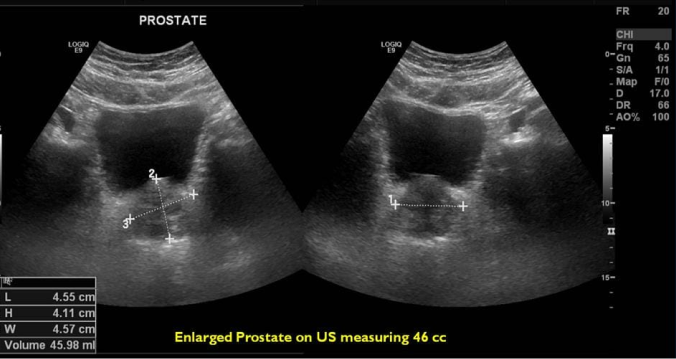
A transrectal ultrasound is a key diagnostic procedure for BPH, utilizing sound waves to create detailed images of the prostate gland. This non-invasive test allows physicians to evaluate prostate size and detect any abnormalities.
Cystoscopy is an essential diagnostic procedure for BPH, involving the insertion of a thin, flexible tube with a camera into the urethra to visually examine the bladder and prostate. This method provides direct visualization, helping to identify obstructions and assess the extent of prostate enlargement.
A prostate biopsy is a critical diagnostic procedure for BPH, involving the extraction of small tissue samples from the prostate gland for microscopic examination. This technique allows for the detailed assessment of prostate cells.
Postvoid residual volume testing is a crucial diagnostic procedure for BPH, measuring the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination using ultrasound or catheterization. This test helps assess the severity of urinary retention.
Treatments for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The dedicated physicians at Pedes Orange County are proud to offer prostate artery embolization (PAE), a cutting-edge treatment for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Developed in Europe and South America, PAE is now common in the United States and successfully addresses urinary symptoms caused by BPH. This unique procedure provides rapid results without affecting your sexual function, setting it apart from other BHP treatments.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)


BPH Specialist in Irvine, CA
Don’t wait to take action on your health. Call Pedes Orange County in Irvine, CA, (949) 387-4724 today to make an appointment with one of our skilled physicians or contact our friendly staff online at your convenience. We look forward to optimizing your health for years to come.
Our Vascular Disease Physicians
The physicians at Pedes Orange County devote their lives to saving limbs and minimizing pain. Our conveniently located, state-of-the-art facility is designed for your comfort and utilizes cutting-edge technology to provide minimally invasive treatments. Our vascular specialists are board-certified and some of the best in Southern California. Personable staff members make every visit a positive experience, with short wait times and an efficient, streamlined process that ensures you leave feeling educated and confident that you are in good hands.

J. Joseph Hewett, M.D.
Vascular Specialist

Neil K. Goldstein, M.D.
Vascular Specialist

Derrick Tran, MD
Vascular Specialist

Mohammad Jaber, M.D.
Vascular Specialist
What to Expect from Your Visit to Pedes

Ultrasound
Advanced ultrasound-guided examination techniques will be used to visualize the veins, arteries, or both, in your legs. This is often used in the diagnostic process to detect the presence and extent of disease.
Consult
Once we review the results of your diagnostic tests, our physicians will collaborate with you to develop a personalized treatment plan, ensuring the best course of treatment for your specific condition.

Treatment
Your treatment plan will be personalized to you and your individual needs. At Pedes, we specialize in minimally invasive procedures and nonsurgical treatments, all of which are performed by our dedicated vascular physicians within the comfort of our state-of-the-art facility.

Follow up
We ensure our patients receive continuous care and support with regular follow-up visits. Each follow-up visit is scheduled at the time of your in-office appointment. Should you have a concern between
appointments, we encourage you to call our office and get scheduled at any time.